You may want to use a self-signed SSL-certificate on your website. This will allow you to save some money, because you do not have to pay for the certificate issued by an approved Certification Authority. However, using self-signed SSL-certificates have some downsides because they may contain a risk for the site and its visitors. There are many other issues associated with using of self-signed SSL-certificates.
Considering the above, it would be wiser not to employ self-signed certificates on your websites. It is highly advisable to spend some money for the purchase of SSL-certificate from a trusted CA. This will save you a lot of money in the long run.
Why should you pay for a certificate?
Buying an SSL-certificate is highly advisable as it is proven to be better option than creating own signature and certificate, which most likely will not work properly. As a result, your website visitors will not be protected therefore they will loose their confidence in your site and products you are offering.
It is not recognizable by web browsers
Existing CA have all required resources that allow them to produce the SSL-certificates as well as checking domain or business ownership and analyze the legitimacy of the website or client’s business. Therefore, web browsers usually trust experienced certificate authority. CAs with a low level of trust will not be able to produce the same level of quality therefore would be not a trustful source. Obviously, you cannot do it.
Considering the above, a certificate which was self-signed, will not be recognized as a trusted certificate. Instead, it will be recognized as ineffective certificate from an untrusted certificate authority. Thus, your SSL-certificate will not be accepted and the browser will issue the warning to all users visiting this website that it is vulnerable to various attacks, and therefore it is better to leave it immediately. Most likely it will result to the loss of users and collapse of your business.
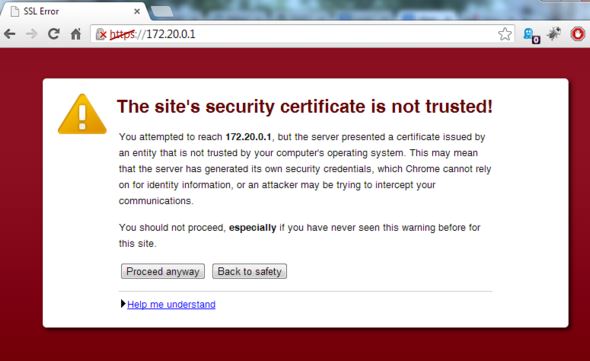
Notice in Chrome that a self-signed certificate is used on the site
Trusted SSL-certificates nowadays are very affordable. Why don’t you try use them?
Falling trust of the visitors
A self-signed certificate will be a cause of warning messages in different web browsers. Your visitors and potential customers will eventually lose trust in your site. As a result, you will lose traffic which will lead to the bankruptcy of the business in the long term.
In case where no warnings from web browsers will be shown, your visitors will still remain uncertain in the site safety, as they are not confident in the quality and reliability of the self-signed certificate. Your identity has not been verified by third-party certification authorities, and visitors may think that you are the fraudster. This will make them concerned that they may face a phishing or a hacker attacks when they make financial transactions online.
In this circumstances most of the visitors will be looking for an alternative site, which will offer a more secure connection.
Self-signed certificates may seem to be a cheaper alternative to an approved SSL-certificates from a trusted CAs. However, due to the negative impact on the site, they can cost you a lot of money, and often the whole business.
You are highly advised to review all the cons before using such certificates on your website.
Do you need SSL certificates? The store of certificates entrusted by years and millions of visitors — LeaderSSL. Buy a certificate from a trusted brand.


Comments